Publications
For the complete list, please see my Google Scholar Profile.
2026
-
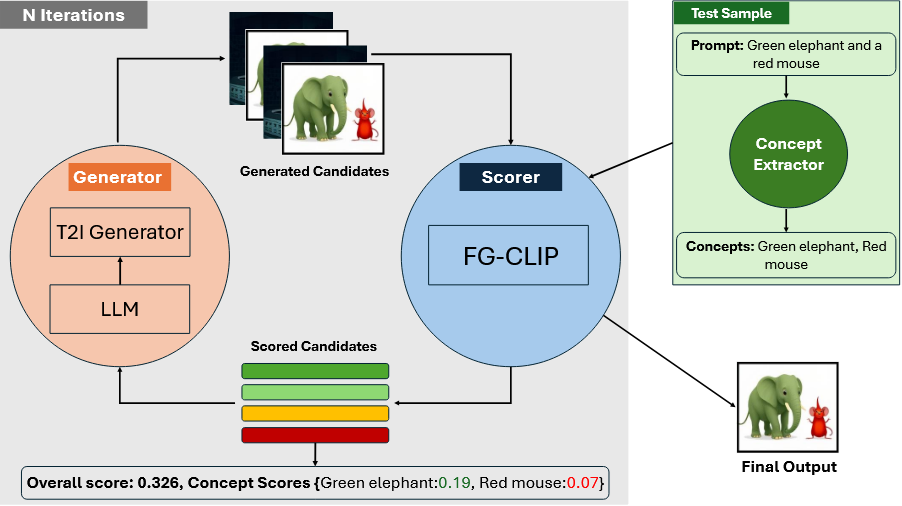 No Concept Left Behind: Test-Time Optimization for Compositional Text-to-Image GenerationAmir M Mansourian*, Mohammad Hossein Sameti*, Arash Marioriyad, Soheil Fadaee Oshyani, Mohammad Hossein Rohban, and Mahdieh Soleymani BaghshahIEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), 2026
No Concept Left Behind: Test-Time Optimization for Compositional Text-to-Image GenerationAmir M Mansourian*, Mohammad Hossein Sameti*, Arash Marioriyad, Soheil Fadaee Oshyani, Mohammad Hossein Rohban, and Mahdieh Soleymani BaghshahIEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), 2026Despite recent advances in text-to-image (T2I) models, they often fail to faithfully render all elements of complex prompts, frequently omitting or misrepresenting specific objects and attributes. Test-time optimization has emerged as a promising approach to address this limitation by refining generation without the need for retraining. In this paper, we propose a fine-grained test-time optimization framework that enhances compositional faithfulness in T2I generation. Unlike most of prior approaches that rely solely on a global image–text similarity score, our method decomposes the input prompt into semantic concepts and evaluates alignment at both the global and concept levels. A fine-grained variant of CLIP is used to compute concept-level correspondence, producing detailed feedback on missing or inaccurate concepts. This feedback is fed into an iterative prompt refinement loop, enabling the large language model to propose improved prompts. Experiments on DrawBench and CompBench prompts demonstrate that our method significantly improves concept coverage and human-judged faithfulness over both standard test-time optimization and the base T2I model.
@article{mansourian2026concept, title = {No Concept Left Behind: Test-Time Optimization for Compositional Text-to-Image Generation}, author = {Mansourian*, Amir M and Sameti*, Mohammad Hossein and Marioriyad, Arash and Fadaee Oshyani, Soheil and Rohban, Mohammad Hossein and Soleymani Baghshah, Mahdieh}, year = {2026}, journal = {IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP)}, } -
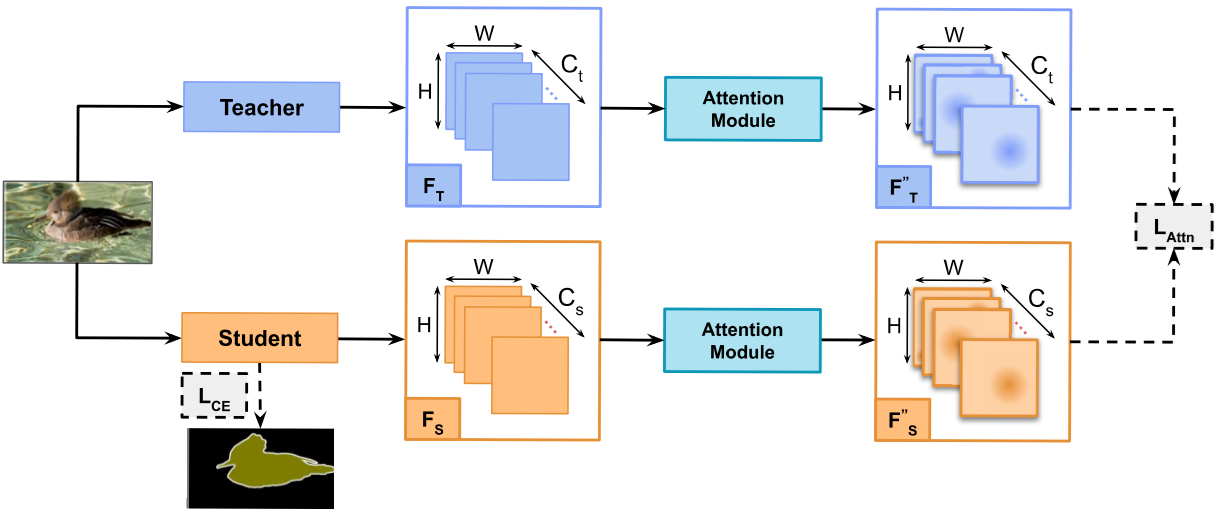 Attention as Geometric Transformation: Revisiting Feature Distillation for Semantic SegmentationAmir M Mansourian, Arya Jalali, Rozhan Ahmadi, and Shohreh KasaeiWinter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, 2026
Attention as Geometric Transformation: Revisiting Feature Distillation for Semantic SegmentationAmir M Mansourian, Arya Jalali, Rozhan Ahmadi, and Shohreh KasaeiWinter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, 2026Knowledge distillation has emerged as an effective strategy for transferring knowledge from large teacher models to compact student models, particularly for semantic segmentation. Most existing feature-based distillation methods rely on complex losses or additional modules to bridge the representational gap between teacher and student networks. In this paper, we revisit feature distillation from a different perspective and show that attention mechanisms can significantly simplify this process. Specifically, we demonstrate that attention modules act as a feature transformation that projects high-dimensional teacher and student representations into a more compact, task-relevant lower-rank latent space, where direct feature alignment becomes more effective. Based on this observation, we propose Attention-guided Feature Distillation (AttnFD), a simple yet effective approach that applies lightweight attention modules to both teacher and student features before enforcing feature similarity using a standard MSE loss. Extensive experiments on multiple semantic segmentation benchmarks show that AttnFD consistently improves student performance across different architectures and datasets, achieving strong gains with negligible computational overhead.
@article{mansourian2026attention, title = {Attention as Geometric Transformation: Revisiting Feature Distillation for Semantic Segmentation}, author = {Mansourian, Amir M and Jalali, Arya and Ahmadi, Rozhan and Kasaei, Shohreh}, journal = {Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision}, year = {2026} }
2025
- ArxivEnriching Knowledge Distillation with Cross-Modal Teacher FusionAmir M Mansourian, Amir Mohammad Babaei, and Shohreh KasaeiarXiv preprint, 2025
Multi-teacher knowledge distillation (KD), a more effective technique than traditional single-teacher methods, transfers knowledge from expert teachers to a compact student model using logit or feature matching. However, most existing approaches lack knowledge diversity, as they rely solely on unimodal visual information, overlooking the potential of cross-modal representations. In this work, we explore the use of CLIP’s vision-language knowledge as a complementary source of supervision for KD, an area that remains largely underexplored. We propose a simple yet effective framework that fuses the logits and features of a conventional teacher with those from CLIP. By incorporating CLIP’s multi-prompt textual guidance, the fused supervision captures both dataset-specific and semantically enriched visual cues. Beyond accuracy, analysis shows that the fused teacher yields more confident and reliable predictions, significantly increasing confident-correct cases while reducing confidently wrong ones. Moreover, fusion with CLIP refines the entire logit distribution, producing semantically meaningful probabilities for non-target classes, thereby improving inter-class consistency and distillation quality. Despite its simplicity, the proposed method, Enriching Knowledge Distillation (RichKD), consistently outperforms most existing baselines across multiple benchmarks and exhibits stronger robustness under distribution shifts and input corruptions.
@article{mansourian2025enriching, title = {Enriching Knowledge Distillation with Cross-Modal Teacher Fusion}, author = {Mansourian, Amir M and Babaei, Amir Mohammad and Kasaei, Shohreh}, year = {2025}, journal = {arXiv preprint} } -
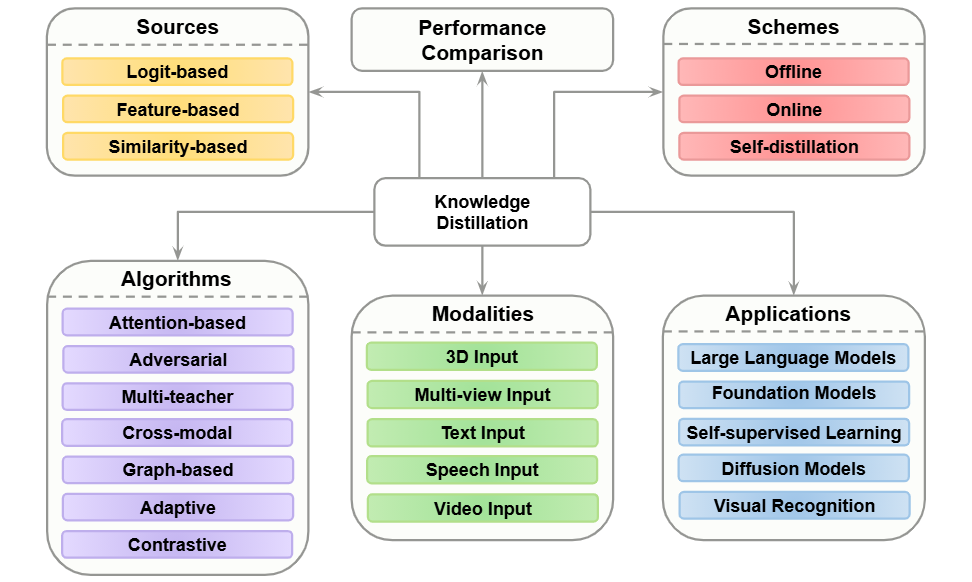 A Comprehensive Survey on Knowledge DistillationAmir M Mansourian, Rozhan Ahmadi, Masoud Ghafouri, Amir Mohammad Babaei, Elaheh Badali Golezani, Zeynab Yasamani Ghamchi, Vida Ramezanian, Alireza Taherian, Kimia Dinashi, Amirali Miri, and Shohreh KasaeiTransactions on Machine Learning Research, 2025
A Comprehensive Survey on Knowledge DistillationAmir M Mansourian, Rozhan Ahmadi, Masoud Ghafouri, Amir Mohammad Babaei, Elaheh Badali Golezani, Zeynab Yasamani Ghamchi, Vida Ramezanian, Alireza Taherian, Kimia Dinashi, Amirali Miri, and Shohreh KasaeiTransactions on Machine Learning Research, 2025Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) have achieved notable performance in the fields of computer vision and natural language processing with various applications in both academia and industry. However, with recent advancements in DNNs and transformer models with a tremendous number of parameters, deploying these large models on edge devices causes serious issues such as high runtime and memory consumption. This is especially concerning with the recent large-scale foundation models, Vision-Language Models (VLMs), and Large Language Models (LLMs). Knowledge Distillation (KD) is one of the prominent techniques proposed to address the aforementioned problems using a teacher-student architecture. More specifically, a lightweight student model is trained using additional knowledge from a cumbersome teacher model. In this work, a comprehensive survey of knowledge distillation methods is proposed. This includes reviewing KD from different aspects: distillation sources, distillation schemes, distillation algorithms, distillation by modalities, applications of distillation, and comparison among existing methods. In contrast to most existing surveys, which are either outdated or simply update former surveys, this work proposes a comprehensive survey with a new point of view and representation structure that categorizes and investigates the most recent methods in knowledge distillation. This survey considers various critically important subcategories, including KD for diffusion models, 3D inputs, foundational models, transformers, and LLMs. Furthermore, existing challenges in KD and possible future research directions are discussed.
@article{mansourian2025comprehensive, title = {A Comprehensive Survey on Knowledge Distillation}, author = {Mansourian, Amir M and Ahmadi, Rozhan and Ghafouri, Masoud and Babaei, Amir Mohammad and Golezani, Elaheh Badali and Ghamchi, Zeynab Yasamani and Ramezanian, Vida and Taherian, Alireza and Dinashi, Kimia and Miri, Amirali and Kasaei, Shohreh}, year = {2025}, journal = {Transactions on Machine Learning Research}, } -
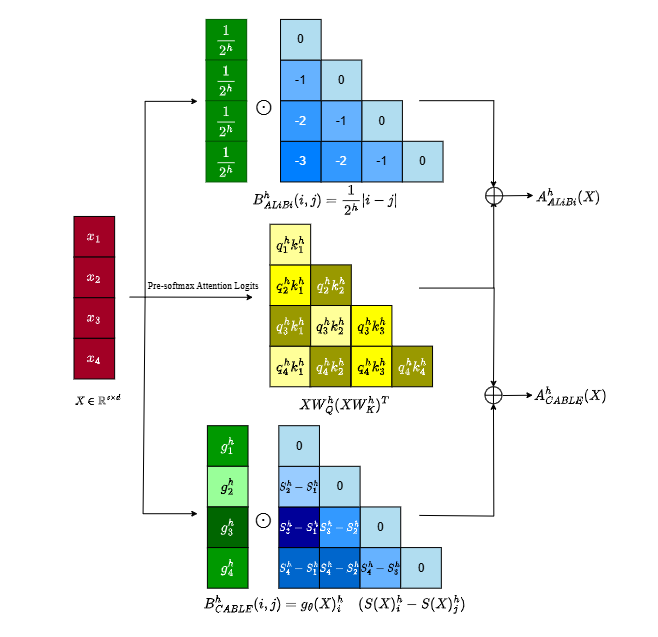 Context-aware Biases for Length ExtrapolationAmir M Mansourian*, Ali Veisi*, and Hamidreza Amirzadeh*Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), 2025
Context-aware Biases for Length ExtrapolationAmir M Mansourian*, Ali Veisi*, and Hamidreza Amirzadeh*Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), 2025Transformers often struggle to generalize to longer sequences than those seen during training—a limitation known as length extrapolation. Most existing Relative Positional Encoding (RPE) methods attempt to address this by introducing either fixed linear biases or globally learned biases, which lack the capacity to adapt to different input contexts. In this work, we propose an additive RPE, Context-Aware Biases for Length Extrapolation (CABLE), a method that learns token-specific, contextaware biases for each attention head in transformers. By dynamically adjusting positional biases based on the input sequence, CABLE overcomes the rigidity of fixed RPEs. When evaluated on sequences longer than originally trained with, GPT-2 Medium (334M parameters) with CABLE achieves lower perplexity than counterparts using other widely adopted positional encoding methods. Additionally, by applying CABLE to the BERT base model we improved performance in long-context retrieval tasks. Our method significantly enhances the extrapolation performance of existing RPE methods tested on the FineWeb-Edu10B and WikiText-103 datasets.
@article{mansourian2025context, title = {Context-aware Biases for Length Extrapolation}, author = {Mansourian*, Amir M and Veisi*, Ali and Amirzadeh*, Hamidreza}, year = {2025}, journal = {Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP)}, } -
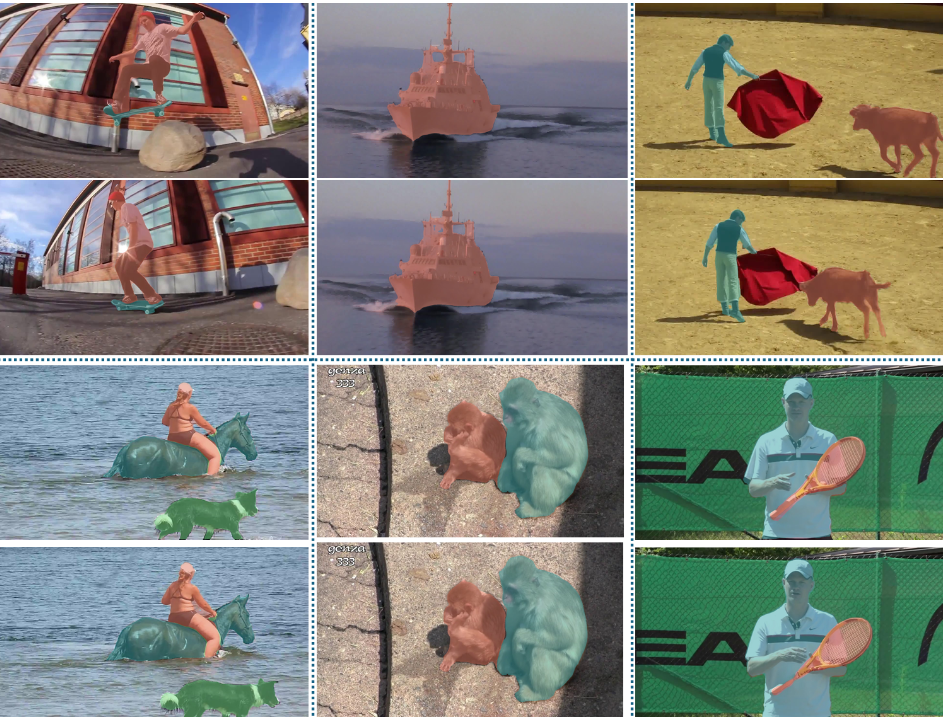 Improving Weakly-supervised Video Instance Segmentation by Leveraging Spatio-temporal ConsistencyFarnoosh Arefi, Amir M Mansourian, and Shohreh KasaeiIEEE Access, 2025
Improving Weakly-supervised Video Instance Segmentation by Leveraging Spatio-temporal ConsistencyFarnoosh Arefi, Amir M Mansourian, and Shohreh KasaeiIEEE Access, 2025The performance of Video Instance Segmentation (VIS) methods has improved significantly with the advent of transformer networks. However, these networks often face challenges in training due to the high annotation cost. To address this, unsupervised and weakly-supervised methods have been developed to reduce the dependency on annotations. This work introduces a novel weakly-supervised method called Eigen-Cluster VIS that, without requiring any mask annotations, achieves competitive accuracy compared to other VIS approaches. This method is based on two key innovations: a Temporal Eigenvalue Loss (TEL) and a clip-level Quality Cluster Coefficient (QCC). The TEL ensures temporal coherence by leveraging the eigenvalues of the Laplacian matrix derived from graph adjacency matrices. By minimizing the mean absolute error between the eigenvalues of adjacent frames, this loss function promotes smooth transitions and stable segmentation boundaries over time, reducing temporal discontinuities and improving overall segmentation quality. The QCC employs the K-means method to ensure the quality of spatio-temporal clusters without relying on ground truth masks. Using the Davies-Bouldin score, the QCC provides an unsupervised measure of feature discrimination, allowing the model to self-evaluate and adapt to varying object distributions, enhancing robustness during the testing phase. These enhancements are computationally efficient and straightforward, offering significant performance gains without additional annotated data. The proposed Eigen-Cluster VIS method is evaluated on the YouTube-Video Instance Segmentation (YouTube-VIS) 2019/2021 and Occluded Video Instance Segmentation (OVIS) datasets, demonstrating that it effectively narrows the performance gap between the fully-supervised and weakly-supervised VIS approaches.
@article{arefi2025eigen, title = {Improving Weakly-supervised Video Instance Segmentation by Leveraging Spatio-temporal Consistency}, author = {Arefi, Farnoosh and Mansourian, Amir M and Kasaei, Shohreh}, year = {2025}, journal = {IEEE Access}, } -
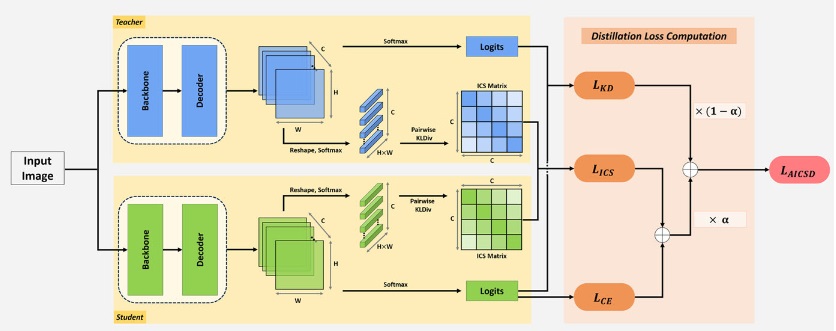 AICSD: Adaptive Inter-Class Similarity Distillation for Semantic SegmentationAmir M Mansourian, Rozhan Ahmadi, and Shohreh KasaeiMultimedia Tools and Applications, 2025
AICSD: Adaptive Inter-Class Similarity Distillation for Semantic SegmentationAmir M Mansourian, Rozhan Ahmadi, and Shohreh KasaeiMultimedia Tools and Applications, 2025In recent years, deep neural networks have achieved remarkable accuracy in computer vision tasks. With inference time being a crucial factor, particularly in dense prediction tasks such as semantic segmentation, knowledge distillation has emerged as a successful technique for improving the accuracy of lightweight student networks. The existing methods often neglect the information in channels and among different classes. To overcome these limitations, this paper proposes a novel method called Inter-Class Similarity Distillation (ICSD) for the purpose of knowledge distillation. The proposed method transfers high-order relations from the teacher network to the student network by independently computing intra-class distributions for each class from network outputs. This is followed by calculating inter-class similarity matrices for distillation using KL divergence between distributions of each pair of classes. To further improve the effectiveness of the proposed method, an Adaptive Loss Weighting (ALW) training strategy is proposed. Unlike existing methods, the ALW strategy gradually reduces the influence of the teacher network towards the end of the training process to account for errors in teacher’s predictions. Extensive experiments conducted on two well-known datasets for semantic segmentation, Cityscapes, Pascal VOC 2012, and COCO, validate the effectiveness of the proposed method in terms of mIoU and pixel accuracy. The proposed method outperforms most of existing knowledge distillation methods as demonstrated by both quantitative and qualitative evaluations.
@article{mansourian2025aicsd, title = {AICSD: Adaptive Inter-Class Similarity Distillation for Semantic Segmentation}, author = {Mansourian, Amir M and Ahmadi, Rozhan and Kasaei, Shohreh}, journal = {Multimedia Tools and Applications}, year = {2025} }
2024
-
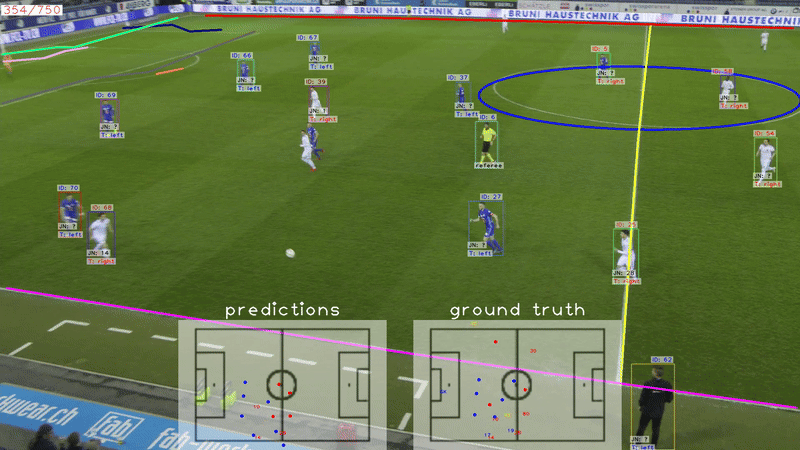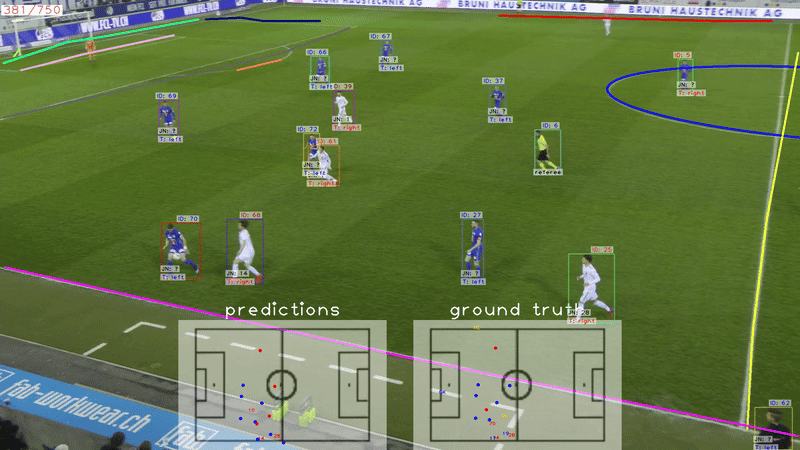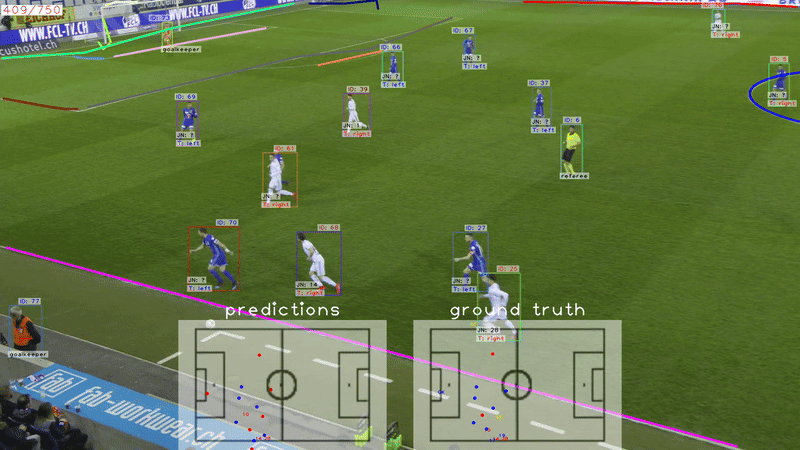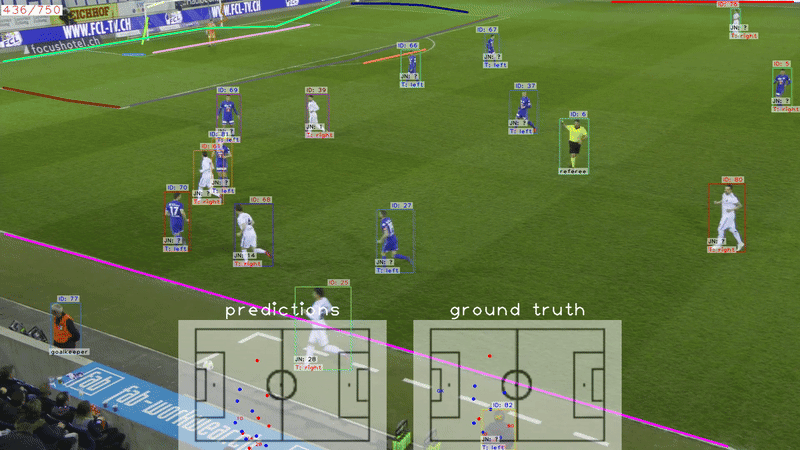 SoccerNet game state reconstruction: End-to-end athlete tracking and identification on a minimapVladimir Somers, Victor Joos, Anthony Cioppa, Silvio Giancola, Seyed Abolfazl Ghasemzadeh, Floriane Magera, Baptiste Standaert, Amir M Mansourian, Xin Zhou, Shohreh Kasaei, and othersIn IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2024
SoccerNet game state reconstruction: End-to-end athlete tracking and identification on a minimapVladimir Somers, Victor Joos, Anthony Cioppa, Silvio Giancola, Seyed Abolfazl Ghasemzadeh, Floriane Magera, Baptiste Standaert, Amir M Mansourian, Xin Zhou, Shohreh Kasaei, and othersIn IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2024Tracking and identifying athletes on the pitch holds acentral role in collecting essential insights from the game,such as estimating the total distance covered by players orunderstanding team tactics. This tracking and identification process is crucial for reconstructing the game state,defined by the athletes’ positions and identities on a 2Dtop-view of the pitch, (i.e. a minimap). However, reconstructing the game state from videos captured by a singlecamera is challenging. It requires understanding the position of the athletes and the viewpoint of the camera to localize and identify players within the field. In this work,we formalize the task of Game State Reconstruction and introduce SoccerNet-GSR, a novel Game State Reconstruction dataset focusing on football videos. SoccerNet-GSRis composed of 200 video sequences of 30 seconds, annotated with 9.37 million line points for pitch localization andcamera calibration, as well as over 2.36 million athlete positions on the pitch with their respective role, team, and jersey number. Furthermore, we introduce GS-HOTA, a novelmetric to evaluate game state reconstruction methods. Finally, we propose and release an end-to-end baseline forgame state reconstruction, bootstrapping the research onthis task. Our experiments show that GSR is a challengingnovel task, which opens the field for future research.
@inproceedings{somers2024soccernet, title = {SoccerNet game state reconstruction: End-to-end athlete tracking and identification on a minimap}, author = {Somers, Vladimir and Joos, Victor and Cioppa, Anthony and Giancola, Silvio and Ghasemzadeh, Seyed Abolfazl and Magera, Floriane and Standaert, Baptiste and Mansourian, Amir M and Zhou, Xin and Kasaei, Shohreh and others}, booktitle = {IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition}, year = {2024} } -
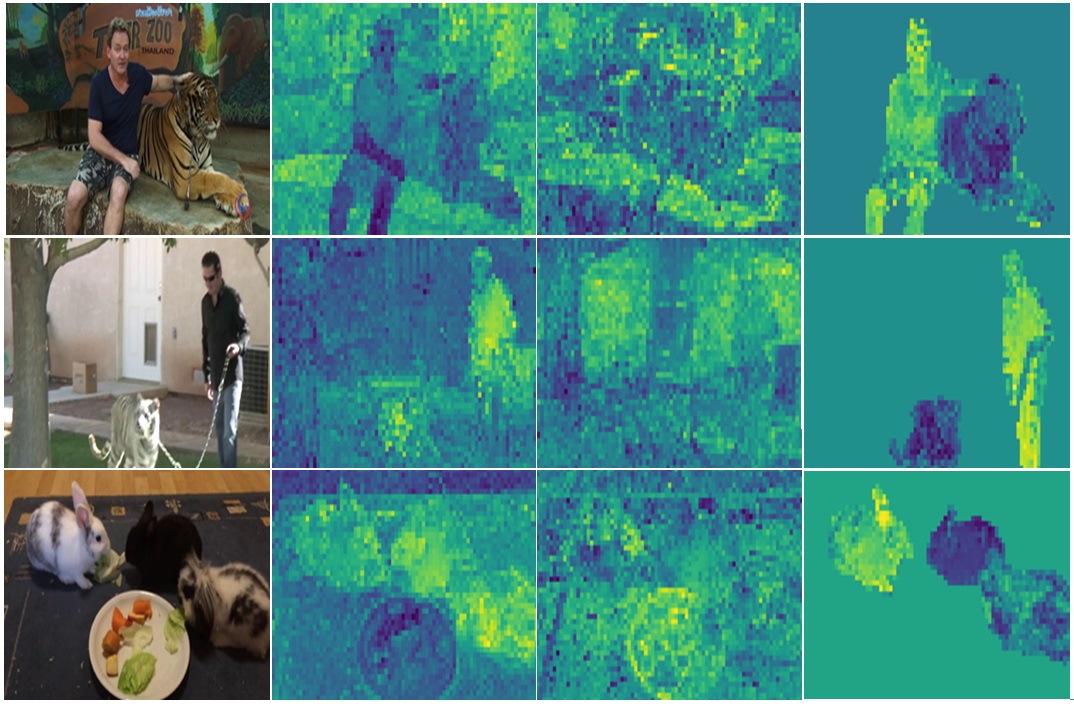 Deep Spectral Improvement for Unsupervised Image Instance SegmentationFarnoosh Arefi, Amir M Mansourian, and Shohreh KasaeiPlos One, 2024
Deep Spectral Improvement for Unsupervised Image Instance SegmentationFarnoosh Arefi, Amir M Mansourian, and Shohreh KasaeiPlos One, 2024Recently, there has been growing interest in deep spectral methods for image localization and segmentation, influenced by traditional spectral segmentation approaches. These methods reframe the image decomposition process as a graph partitioning task by extracting features using self-supervised learning and utilizing the Laplacian of the affinity matrix to obtain eigensegments. However, instance segmentation has received less attention compared to other tasks within the context of deep spectral methods. This paper addresses the fact that not all channels of the feature map extracted from a selfsupervised backbone contain sufficient information for instance segmentation purposes. In fact, some channels are noisy and hinder the accuracy of the task. To overcome this issue, this paper proposes two channel reduction modules: Noise Channel Reduction (NCR) and Deviation-based Channel Reduction (DCR). The NCR retains channels with lower entropy, as they are less likely to be noisy, while DCR prunes channels with low standard deviation, as they lack sufficient information for effective instance segmentation. Furthermore, the paper demonstrates that the dot product, commonly used in deep spectral methods, is not su itable for instance segmentation due to its sensitivity to feature map values, potentially leading to incorrect instance segments. To address this issue, a new similarity metric called Bray-Curtis over Chebyshev (BoC) is proposed. It takes into account the distribution of features in addition to their values, providing a more robust similarity measure for instance segmentation. Quantitative and qualitative results on the Youtube-VIS2019 dataset highlight the improvements achieved by the proposed channel reduction methods and the use of BoC instead of the conventional dot product for creating the affinity matrix. These improvements are observed in terms of mean Intersection over Union (mIoU) and extracted instance segments, demonstrating enhanced instance segmentation performance.
@article{arefi2024deep, title = {Deep Spectral Improvement for Unsupervised Image Instance Segmentation}, author = {Arefi, Farnoosh and Mansourian, Amir M and Kasaei, Shohreh}, year = {2024}, journal = {Plos One} } -
 Rethinking RAFT for Efficient Optical FlowNavid Eslami, Farnoosh Arefi, Amir M Mansourian, and Shohreh KasaeiInternational Conference on Machine Vision and Image Processing (MVIP), 2024
Rethinking RAFT for Efficient Optical FlowNavid Eslami, Farnoosh Arefi, Amir M Mansourian, and Shohreh KasaeiInternational Conference on Machine Vision and Image Processing (MVIP), 2024Despite significant progress in deep learning-based optical flow methods, accurately estimating large displacements and repetitive patterns remains a challenge. The limitations of local features and similarity search patterns used in these algorithms contribute to this issue. Additionally, some existing methods suffer from slow runtime and excessive graphic memory consumption. To address these problems, this paper proposes a novel approach based on the RAFT framework. The proposed Attention-based Feature Localization (AFL) approach incorporates the attention mechanism to handle global feature extraction and address repetitive patterns. It introduces an operator for matching pixels with corresponding counterparts in the second frame and assigning accurate flow values. Furthermore, an Amorphous Lookup Operator (ALO) is proposed to enhance convergence speed and improve RAFTs ability to handle large displacements by reducing data redundancy in its search operator and expanding the search space for similarity extraction. The proposed method, Efficient RAFT (Ef-RAFT),achieves significant improvements of 10% on the Sintel dataset and 5% on the KITTI dataset over RAFT. Remarkably, these enhancements are attained with a modest 33% reduction in speed and a mere 13% increase in memory usage.
@article{eslami2024rethinking, title = {Rethinking RAFT for Efficient Optical Flow}, author = {Eslami, Navid and Arefi, Farnoosh and Mansourian, Amir M and Kasaei, Shohreh}, year = {2024}, journal = {International Conference on Machine Vision and Image Processing (MVIP)} }
2023
-
 Multi-task Learning for Joint Re-identification, Team Affiliation, and Role Classification for Sports Visual TrackingAmir M Mansourian, Vladimir Somers, Christophe De Vleeschouwer, and Shohreh KasaeiIn Proceedings of the 6th International Workshop on Multimedia Content Analysis in Sports, 2023
Multi-task Learning for Joint Re-identification, Team Affiliation, and Role Classification for Sports Visual TrackingAmir M Mansourian, Vladimir Somers, Christophe De Vleeschouwer, and Shohreh KasaeiIn Proceedings of the 6th International Workshop on Multimedia Content Analysis in Sports, 2023Effective tracking and re-identification of players is essential foranalyzing soccer videos. But, it is a challenging task due to the non-linear motion of players, the similarity in appearance of playersfrom the same team, and frequent occlusions. Therefore, the abilityto extract meaningful embeddings to represent players is crucialin developing an effective tracking and re-identification system.In this paper, a multi-purpose part-based person representationmethod, called PRTreID, is proposed that performs three tasks ofrole classification, team affiliation, and re-identification, simultane-ously. In contrast to available literature, a single network is trainedwith multi-task supervision to solve all three tasks, jointly. The pro-posed joint method is computationally efficient due to the sharedbackbone. Also, the multi-task learning leads to richer and morediscriminative representations, as demonstrated by both quanti-tative and qualitative results. To demonstrate the effectiveness ofPRTreID, it is integrated with a state-of-the-art tracking method,using a part-based post-processing module to handle long-termtracking. The proposed tracking method, outperforms all existingtracking methods on the challenging SoccerNet tracking dataset.
@inproceedings{mansourian2023multi, title = {Multi-task Learning for Joint Re-identification, Team Affiliation, and Role Classification for Sports Visual Tracking}, author = {Mansourian, Amir M and Somers, Vladimir and De Vleeschouwer, Christophe and Kasaei, Shohreh}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the 6th International Workshop on Multimedia Content Analysis in Sports}, pages = {103--112}, year = {2023} } -
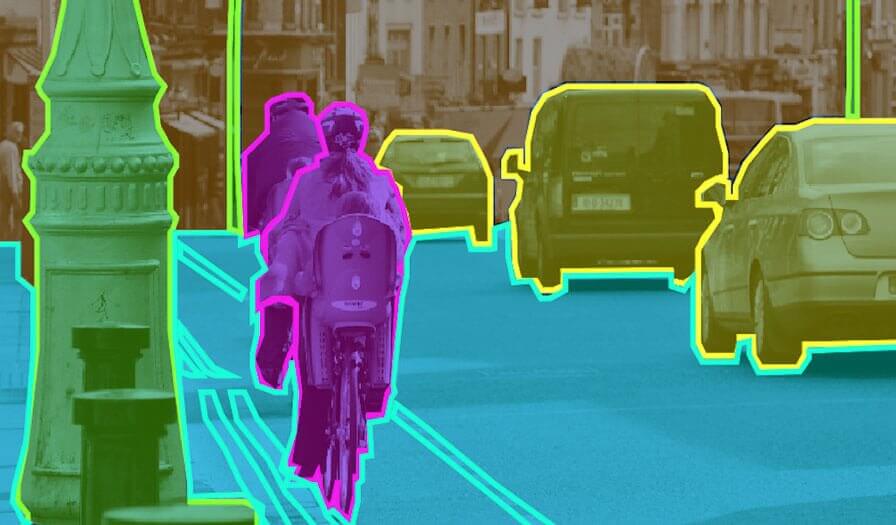 An Efficient Knowledge Distillation Architecture for Real-time Semantic SegmentationAmir M Mansourian, Nader Karimi, and Shohreh KasaeiAUT Journal of Modeling and Simulation, 2023
An Efficient Knowledge Distillation Architecture for Real-time Semantic SegmentationAmir M Mansourian, Nader Karimi, and Shohreh KasaeiAUT Journal of Modeling and Simulation, 2023In recent years, Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) have made significant strides in the field of segmentation, particularly in semantic segmentation where both accuracy and efficiency are crucial. However, despite their high accuracy, these deep networks are not practical for real-time use due to their low inference speed. This issue has prompted researchers to explore various techniques to improve the efficiency of CNNs. One such technique is knowledge distillation, which involves transferring knowledge from a larger, cumbersome (teacher) model to a smaller, more compact (student) model. This paper proposes a simple yet efficient approach to address the issue of low inference speed in CNNs using knowledge distillation. The proposed method involves distilling knowledge from the feature maps of the teacher model to guide the learning of the student model. The approach uses a straightforward technique known as pixel-wise distillation to transfer the feature maps of the last convolution layer of the teacher model to the student model. Additionally, a pair-wise distillation technique is used to transfer pair-wise similarities of the intermediate layers. To validate the effectiveness of the proposed method, extensive experiments were conducted on the PascalVoc 2012 dataset using a state-of-the art DeepLabV3+ segmentation network with different backbone architectures. The results showed that the proposed method achieved a balanced mean Intersection over Union (mIoU) and training time.
@article{mansourian2023anefficient, author = {Mansourian, Amir M and Karimi, Nader and Kasaei, Shohreh}, title = {An Efficient Knowledge Distillation Architecture for Real-time Semantic Segmentation}, journal = {AUT Journal of Modeling and Simulation}, year = {2023}, }